서버 사이드 호출
이 페이지는 PageTurner AI로 번역되었습니다(베타). 프로젝트 공식 승인을 받지 않았습니다. 오류를 발견하셨나요? 문제 신고 →
동일한 서버에 호스팅된 프로시저를 직접 호출해야 하는 경우, createCallerFactory()를 사용할 수 있습니다. 이는 서버 사이드 호출과 tRPC 프로시저의 통합 테스트에 유용합니다.
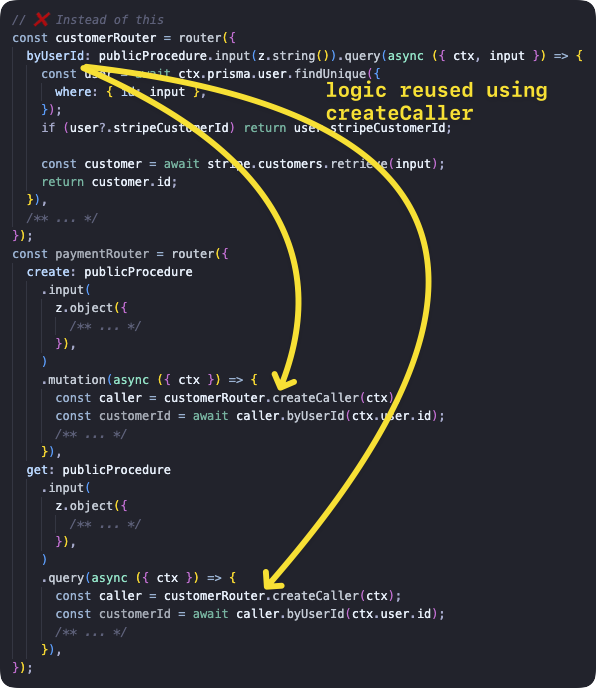
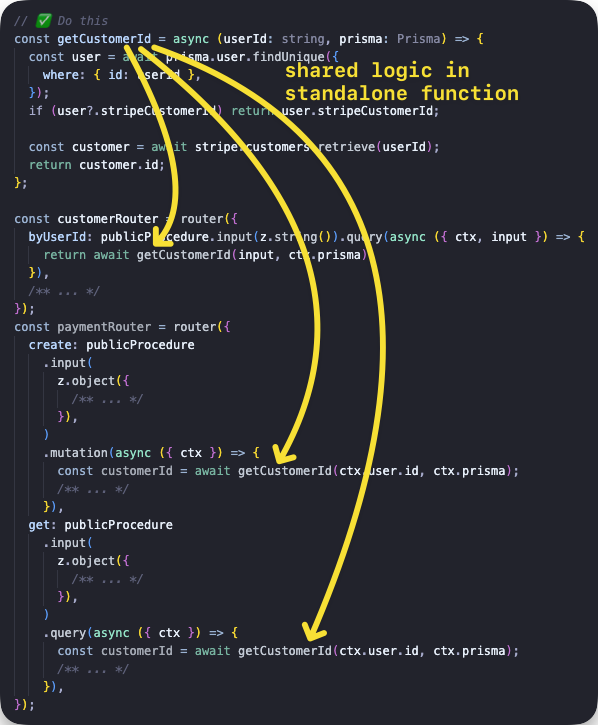
createCaller는 다른 프로시저 내부에서 프로시저를 호출하는 데 사용되어서는 안 됩니다. 이는 (잠재적으로) 컨텍스트를 다시 생성하고, 모든 미들웨어를 실행하며, 입력값을 검증하는 오버헤드를 발생시킵니다. 이러한 작업들은 모두 현재 프로시저에서 이미 완료되었습니다. 대신 공유 로직을 별도의 함수로 추출하여 프로시저 내부에서 호출하는 방식을 사용해야 합니다.
호출자 생성
t.createCallerFactory 함수를 사용하면 모든 라우터의 서버 사이드 호출자를 생성할 수 있습니다. 먼저 호출하려는 라우터를 인자로 createCallerFactory를 호출한 다음, 반환된 함수에 후속 프로시저 호출을 위한 Context를 전달합니다.
기본 예제
게시물 목록을 조회하는 쿼리와 게시물을 추가하는 뮤테이션으로 라우터를 생성한 후 각 메서드를 호출합니다.
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';typeContext = {foo : string;};constt =initTRPC .context <Context >().create ();constpublicProcedure =t .procedure ;const {createCallerFactory ,router } =t ;interfacePost {id : string;title : string;}constposts :Post [] = [{id : '1',title : 'Hello world',},];constappRouter =router ({post :router ({add :publicProcedure .input (z .object ({title :z .string ().min (2),}),).mutation ((opts ) => {constpost :Post = {...opts .input ,id : `${Math .random ()}`,};posts .push (post );returnpost ;}),list :publicProcedure .query (() =>posts ),}),});// 1. create a caller-function for your routerconstcreateCaller =createCallerFactory (appRouter );// 2. create a caller using your `Context`constcaller =createCaller ({foo : 'bar',});// 3. use the caller to add and list postsconstaddedPost = awaitcaller .post .add ({title : 'How to make server-side call in tRPC',});constpostList = awaitcaller .post .list ();
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';typeContext = {foo : string;};constt =initTRPC .context <Context >().create ();constpublicProcedure =t .procedure ;const {createCallerFactory ,router } =t ;interfacePost {id : string;title : string;}constposts :Post [] = [{id : '1',title : 'Hello world',},];constappRouter =router ({post :router ({add :publicProcedure .input (z .object ({title :z .string ().min (2),}),).mutation ((opts ) => {constpost :Post = {...opts .input ,id : `${Math .random ()}`,};posts .push (post );returnpost ;}),list :publicProcedure .query (() =>posts ),}),});// 1. create a caller-function for your routerconstcreateCaller =createCallerFactory (appRouter );// 2. create a caller using your `Context`constcaller =createCaller ({foo : 'bar',});// 3. use the caller to add and list postsconstaddedPost = awaitcaller .post .add ({title : 'How to make server-side call in tRPC',});constpostList = awaitcaller .post .list ();
통합 테스트에서의 예제 사용법
다음에서 가져옴: https://github.com/trpc/examples-next-prisma-starter/blob/main/src/server/routers/post.test.ts
ts
ts
router.createCaller()
router.createCaller({}) 함수(첫 번째 인자는 Context)를 사용하면 RouterCaller 인스턴스를 가져올 수 있습니다.
입력 쿼리 예제
입력 쿼리가 포함된 라우터를 생성한 후 비동기 greeting 프로시저를 호출하여 결과를 얻습니다.
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';constt =initTRPC .create ();constrouter =t .router ({// Create procedure at path 'greeting'greeting :t .procedure .input (z .object ({name :z .string () })).query ((opts ) => `Hello ${opts .input .name }`),});constcaller =router .createCaller ({});constresult = awaitcaller .greeting ({name : 'tRPC' });
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';constt =initTRPC .create ();constrouter =t .router ({// Create procedure at path 'greeting'greeting :t .procedure .input (z .object ({name :z .string () })).query ((opts ) => `Hello ${opts .input .name }`),});constcaller =router .createCaller ({});constresult = awaitcaller .greeting ({name : 'tRPC' });
뮤테이션 예제
뮤테이션이 포함된 라우터를 생성한 후 비동기 post 프로시저를 호출하여 결과를 얻습니다.
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';constposts = ['One', 'Two', 'Three'];constt =initTRPC .create ();constrouter =t .router ({post :t .router ({add :t .procedure .input (z .string ()).mutation ((opts ) => {posts .push (opts .input );returnposts ;}),}),});constcaller =router .createCaller ({});constresult = awaitcaller .post .add ('Four');
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';constposts = ['One', 'Two', 'Three'];constt =initTRPC .create ();constrouter =t .router ({post :t .router ({add :t .procedure .input (z .string ()).mutation ((opts ) => {posts .push (opts .input );returnposts ;}),}),});constcaller =router .createCaller ({});constresult = awaitcaller .post .add ('Four');
미들웨어와 함께하는 Context 예제
secret 프로시저 실행 전 컨텍스트를 확인하는 미들웨어를 생성합니다. 아래 두 예제 중 전자는 컨텍스트가 미들웨어 로직에 맞지 않아 실패하고, 후자는 올바르게 작동합니다.
모든 프로시저 호출 전에 미들웨어가 수행됩니다.
tsinitTRPC ,TRPCError } from '@trpc/server';typeContext = {user ?: {id : string;};};constt =initTRPC .context <Context >().create ();constprotectedProcedure =t .procedure .use ((opts ) => {const {ctx } =opts ;if (!ctx .user ) {throw newTRPCError ({code : 'UNAUTHORIZED',message : 'You are not authorized',});}returnopts .next ({ctx : {// Infers that the `user` is non-nullableuser :ctx .user ,},});});constrouter =t .router ({secret :protectedProcedure .query ((opts ) =>opts .ctx .user ),});{// ❌ this will return an error because there isn't the right context paramconstcaller =router .createCaller ({});constresult = awaitcaller .secret ();}{// ✅ this will work because user property is present inside context paramconstauthorizedCaller =router .createCaller ({user : {id : 'KATT',},});constresult = awaitauthorizedCaller .secret ();}
tsinitTRPC ,TRPCError } from '@trpc/server';typeContext = {user ?: {id : string;};};constt =initTRPC .context <Context >().create ();constprotectedProcedure =t .procedure .use ((opts ) => {const {ctx } =opts ;if (!ctx .user ) {throw newTRPCError ({code : 'UNAUTHORIZED',message : 'You are not authorized',});}returnopts .next ({ctx : {// Infers that the `user` is non-nullableuser :ctx .user ,},});});constrouter =t .router ({secret :protectedProcedure .query ((opts ) =>opts .ctx .user ),});{// ❌ this will return an error because there isn't the right context paramconstcaller =router .createCaller ({});constresult = awaitcaller .secret ();}{// ✅ this will work because user property is present inside context paramconstauthorizedCaller =router .createCaller ({user : {id : 'KATT',},});constresult = awaitauthorizedCaller .secret ();}
Next.js API 엔드포인트 예제
이 예제는 Next.js API 엔드포인트에서 호출자를 사용하는 방법을 보여줍니다. tRPC는 이미 API 엔드포인트를 생성하므로, 이 파일은 사용자 정의 엔드포인트에서 프로시저를 호출하는 방법을 설명하기 위한 목적으로만 제공됩니다.
tsTRPCError } from '@trpc/server';import {getHTTPStatusCodeFromError } from '@trpc/server/http';import {appRouter } from '~/server/routers/_app';import type {NextApiRequest ,NextApiResponse } from 'next';typeResponseData = {data ?: {postTitle : string;};error ?: {message : string;};};export default async (req :NextApiRequest ,res :NextApiResponse <ResponseData >,) => {/** We want to simulate an error, so we pick a post ID that does not exist in the database. */constpostId = `this-id-does-not-exist-${Math .random ()}`;constcaller =appRouter .createCaller ({});try {// the server-side callconstpostResult = awaitcaller .post .byId ({id :postId });res .status (200).json ({data : {postTitle :postResult .title } });} catch (cause ) {// If this a tRPC error, we can extract additional information.if (cause instanceofTRPCError ) {// We can get the specific HTTP status code coming from tRPC (e.g. 404 for `NOT_FOUND`).consthttpStatusCode =getHTTPStatusCodeFromError (cause );res .status (httpStatusCode ).json ({error : {message :cause .message } });return;}// This is not a tRPC error, so we don't have specific information.res .status (500).json ({error : {message : `Error while accessing post with ID ${postId }` },});}};
tsTRPCError } from '@trpc/server';import {getHTTPStatusCodeFromError } from '@trpc/server/http';import {appRouter } from '~/server/routers/_app';import type {NextApiRequest ,NextApiResponse } from 'next';typeResponseData = {data ?: {postTitle : string;};error ?: {message : string;};};export default async (req :NextApiRequest ,res :NextApiResponse <ResponseData >,) => {/** We want to simulate an error, so we pick a post ID that does not exist in the database. */constpostId = `this-id-does-not-exist-${Math .random ()}`;constcaller =appRouter .createCaller ({});try {// the server-side callconstpostResult = awaitcaller .post .byId ({id :postId });res .status (200).json ({data : {postTitle :postResult .title } });} catch (cause ) {// If this a tRPC error, we can extract additional information.if (cause instanceofTRPCError ) {// We can get the specific HTTP status code coming from tRPC (e.g. 404 for `NOT_FOUND`).consthttpStatusCode =getHTTPStatusCodeFromError (cause );res .status (httpStatusCode ).json ({error : {message :cause .message } });return;}// This is not a tRPC error, so we don't have specific information.res .status (500).json ({error : {message : `Error while accessing post with ID ${postId }` },});}};
오류 처리
createFactoryCaller 및 createCaller 함수는 onError 옵션을 통해 오류 핸들러를 전달받을 수 있습니다. 이는 TRPCError로 래핑되지 않은 오류를 발생시키거나 다른 방식으로 오류에 대응하는 데 사용됩니다. createCallerFactory에 전달된 핸들러는 createCaller에 전달된 핸들러보다 먼저 호출됩니다. 핸들러는 shape 필드를 제외하고 오류 포매터와 동일한 인자로 호출됩니다.
ts
ts
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';constt =initTRPC .context <{foo ?: 'bar';}>().create ();constrouter =t .router ({greeting :t .procedure .input (z .object ({name :z .string () })).query ((opts ) => {if (opts .input .name === 'invalid') {throw newError ('Invalid name');}return `Hello ${opts .input .name }`;}),});constcaller =router .createCaller ({/* context */},{onError : (opts ) => {console .error ('An error occurred:',opts .error );},},);// The following will log "An error occurred: Error: Invalid name", and then throw a plain error// with the message "This is a custom error"awaitcaller .greeting ({name : 'invalid' });
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';constt =initTRPC .context <{foo ?: 'bar';}>().create ();constrouter =t .router ({greeting :t .procedure .input (z .object ({name :z .string () })).query ((opts ) => {if (opts .input .name === 'invalid') {throw newError ('Invalid name');}return `Hello ${opts .input .name }`;}),});constcaller =router .createCaller ({/* context */},{onError : (opts ) => {console .error ('An error occurred:',opts .error );},},);// The following will log "An error occurred: Error: Invalid name", and then throw a plain error// with the message "This is a custom error"awaitcaller .greeting ({name : 'invalid' });