Anrop på serversidan
Denna sida har översatts av PageTurner AI (beta). Inte officiellt godkänd av projektet. Hittade du ett fel? Rapportera problem →
Du kan behöva anropa dina procedurer direkt från samma server där de är hostade. createCallerFactory() kan användas för detta. Det är användbart för server-anrop och integrationstester av dina tRPC-procedurer.
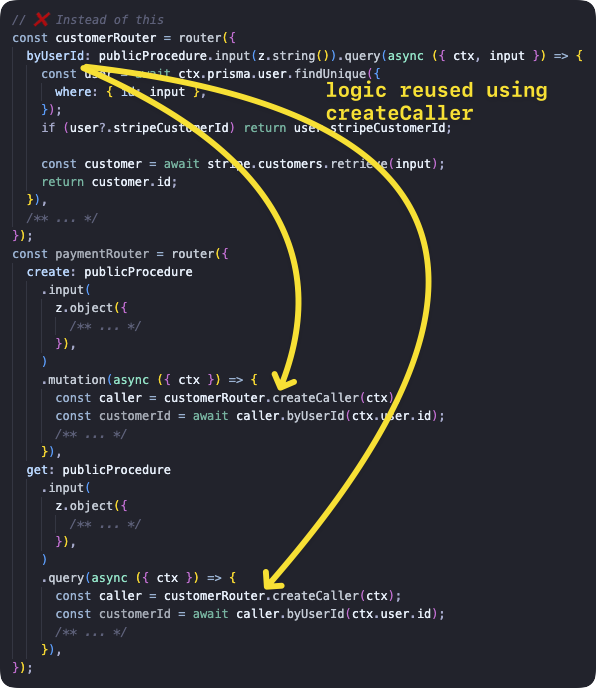
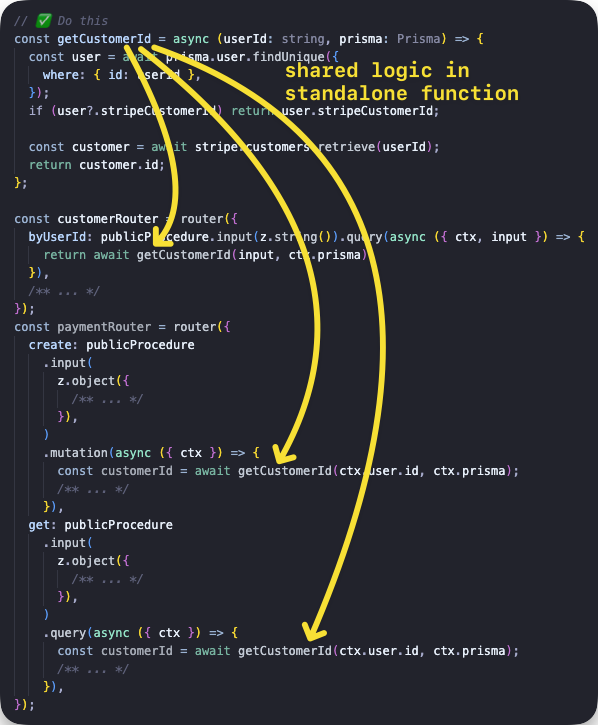
createCaller bör inte användas för att anropa procedurer från andra procedurer. Det skapar onödig overhead genom att (potentiellt) skapa kontext igen, köra alla middlewares och validera input - allt detta har redan gjorts i den aktuella proceduren. Istället bör du extrahera den delade logiken till en separat funktion och anropa den från procedurerna, så här:
Skapa anropare
Med funktionen t.createCallerFactory kan du skapa en serversidan-anropare för valfri router. Du anropar först createCallerFactory med routern du vill anropa som argument, sedan returneras en funktion där du kan skicka in en Context för efterföljande procedure-anrop.
Grundläggande exempel
Vi skapar routern med en query för att lista inlägg och en mutation för att lägga till inlägg, sedan anropar vi varje metod.
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';typeContext = {foo : string;};constt =initTRPC .context <Context >().create ();constpublicProcedure =t .procedure ;const {createCallerFactory ,router } =t ;interfacePost {id : string;title : string;}constposts :Post [] = [{id : '1',title : 'Hello world',},];constappRouter =router ({post :router ({add :publicProcedure .input (z .object ({title :z .string ().min (2),}),).mutation ((opts ) => {constpost :Post = {...opts .input ,id : `${Math .random ()}`,};posts .push (post );returnpost ;}),list :publicProcedure .query (() =>posts ),}),});// 1. create a caller-function for your routerconstcreateCaller =createCallerFactory (appRouter );// 2. create a caller using your `Context`constcaller =createCaller ({foo : 'bar',});// 3. use the caller to add and list postsconstaddedPost = awaitcaller .post .add ({title : 'How to make server-side call in tRPC',});constpostList = awaitcaller .post .list ();
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';typeContext = {foo : string;};constt =initTRPC .context <Context >().create ();constpublicProcedure =t .procedure ;const {createCallerFactory ,router } =t ;interfacePost {id : string;title : string;}constposts :Post [] = [{id : '1',title : 'Hello world',},];constappRouter =router ({post :router ({add :publicProcedure .input (z .object ({title :z .string ().min (2),}),).mutation ((opts ) => {constpost :Post = {...opts .input ,id : `${Math .random ()}`,};posts .push (post );returnpost ;}),list :publicProcedure .query (() =>posts ),}),});// 1. create a caller-function for your routerconstcreateCaller =createCallerFactory (appRouter );// 2. create a caller using your `Context`constcaller =createCaller ({foo : 'bar',});// 3. use the caller to add and list postsconstaddedPost = awaitcaller .post .add ({title : 'How to make server-side call in tRPC',});constpostList = awaitcaller .post .list ();
Exempelanvändning i integrationstest
Hämtat från https://github.com/trpc/examples-next-prisma-starter/blob/main/src/server/routers/post.test.ts
ts
ts
router.createCaller()
Med funktionen router.createCaller({}) (första argumentet är Context) får vi en instans av RouterCaller.
Exempel med input-query
Vi skapar routern med en input-query, sedan anropar vi den asynkrona proceduren greeting för att få resultatet.
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';constt =initTRPC .create ();constrouter =t .router ({// Create procedure at path 'greeting'greeting :t .procedure .input (z .object ({name :z .string () })).query ((opts ) => `Hello ${opts .input .name }`),});constcaller =router .createCaller ({});constresult = awaitcaller .greeting ({name : 'tRPC' });
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';constt =initTRPC .create ();constrouter =t .router ({// Create procedure at path 'greeting'greeting :t .procedure .input (z .object ({name :z .string () })).query ((opts ) => `Hello ${opts .input .name }`),});constcaller =router .createCaller ({});constresult = awaitcaller .greeting ({name : 'tRPC' });
Mutationsexempel
Vi skapar routern med en mutation, sedan anropar vi den asynkrona proceduren post för att få resultatet.
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';constposts = ['One', 'Two', 'Three'];constt =initTRPC .create ();constrouter =t .router ({post :t .router ({add :t .procedure .input (z .string ()).mutation ((opts ) => {posts .push (opts .input );returnposts ;}),}),});constcaller =router .createCaller ({});constresult = awaitcaller .post .add ('Four');
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';constposts = ['One', 'Two', 'Three'];constt =initTRPC .create ();constrouter =t .router ({post :t .router ({add :t .procedure .input (z .string ()).mutation ((opts ) => {posts .push (opts .input );returnposts ;}),}),});constcaller =router .createCaller ({});constresult = awaitcaller .post .add ('Four');
Exempel med kontext och middleware
Vi skapar en middleware för att kontrollera kontexten innan secret-proceduren körs. Nedan visas två exempel: det första misslyckas eftersom kontexten inte matchar middleware-logiken, det andra fungerar korrekt.
Middlewares körs innan några procedurer anropas.
tsinitTRPC ,TRPCError } from '@trpc/server';typeContext = {user ?: {id : string;};};constt =initTRPC .context <Context >().create ();constprotectedProcedure =t .procedure .use ((opts ) => {const {ctx } =opts ;if (!ctx .user ) {throw newTRPCError ({code : 'UNAUTHORIZED',message : 'You are not authorized',});}returnopts .next ({ctx : {// Infers that the `user` is non-nullableuser :ctx .user ,},});});constrouter =t .router ({secret :protectedProcedure .query ((opts ) =>opts .ctx .user ),});{// ❌ this will return an error because there isn't the right context paramconstcaller =router .createCaller ({});constresult = awaitcaller .secret ();}{// ✅ this will work because user property is present inside context paramconstauthorizedCaller =router .createCaller ({user : {id : 'KATT',},});constresult = awaitauthorizedCaller .secret ();}
tsinitTRPC ,TRPCError } from '@trpc/server';typeContext = {user ?: {id : string;};};constt =initTRPC .context <Context >().create ();constprotectedProcedure =t .procedure .use ((opts ) => {const {ctx } =opts ;if (!ctx .user ) {throw newTRPCError ({code : 'UNAUTHORIZED',message : 'You are not authorized',});}returnopts .next ({ctx : {// Infers that the `user` is non-nullableuser :ctx .user ,},});});constrouter =t .router ({secret :protectedProcedure .query ((opts ) =>opts .ctx .user ),});{// ❌ this will return an error because there isn't the right context paramconstcaller =router .createCaller ({});constresult = awaitcaller .secret ();}{// ✅ this will work because user property is present inside context paramconstauthorizedCaller =router .createCaller ({user : {id : 'KATT',},});constresult = awaitauthorizedCaller .secret ();}
Exempel för Next.js API-endpoint
Det här exemplet visar hur du använder anroparen i en Next.js API-endpoint. tRPC skapar redan API-endpoints åt dig, så den här filen är endast avsedd att visa hur du anropar en procedur från en annan anpassad endpoint.
tsTRPCError } from '@trpc/server';import {getHTTPStatusCodeFromError } from '@trpc/server/http';import {appRouter } from '~/server/routers/_app';import type {NextApiRequest ,NextApiResponse } from 'next';typeResponseData = {data ?: {postTitle : string;};error ?: {message : string;};};export default async (req :NextApiRequest ,res :NextApiResponse <ResponseData >,) => {/** We want to simulate an error, so we pick a post ID that does not exist in the database. */constpostId = `this-id-does-not-exist-${Math .random ()}`;constcaller =appRouter .createCaller ({});try {// the server-side callconstpostResult = awaitcaller .post .byId ({id :postId });res .status (200).json ({data : {postTitle :postResult .title } });} catch (cause ) {// If this a tRPC error, we can extract additional information.if (cause instanceofTRPCError ) {// We can get the specific HTTP status code coming from tRPC (e.g. 404 for `NOT_FOUND`).consthttpStatusCode =getHTTPStatusCodeFromError (cause );res .status (httpStatusCode ).json ({error : {message :cause .message } });return;}// This is not a tRPC error, so we don't have specific information.res .status (500).json ({error : {message : `Error while accessing post with ID ${postId }` },});}};
tsTRPCError } from '@trpc/server';import {getHTTPStatusCodeFromError } from '@trpc/server/http';import {appRouter } from '~/server/routers/_app';import type {NextApiRequest ,NextApiResponse } from 'next';typeResponseData = {data ?: {postTitle : string;};error ?: {message : string;};};export default async (req :NextApiRequest ,res :NextApiResponse <ResponseData >,) => {/** We want to simulate an error, so we pick a post ID that does not exist in the database. */constpostId = `this-id-does-not-exist-${Math .random ()}`;constcaller =appRouter .createCaller ({});try {// the server-side callconstpostResult = awaitcaller .post .byId ({id :postId });res .status (200).json ({data : {postTitle :postResult .title } });} catch (cause ) {// If this a tRPC error, we can extract additional information.if (cause instanceofTRPCError ) {// We can get the specific HTTP status code coming from tRPC (e.g. 404 for `NOT_FOUND`).consthttpStatusCode =getHTTPStatusCodeFromError (cause );res .status (httpStatusCode ).json ({error : {message :cause .message } });return;}// This is not a tRPC error, so we don't have specific information.res .status (500).json ({error : {message : `Error while accessing post with ID ${postId }` },});}};
Felhantering
Funktionerna createFactoryCaller och createCaller kan ta en felhanterare via alternativet onError. Detta kan användas för att kasta fel som inte är inslagna i TRPCError, eller hantera fel på annat sätt. Alla hanterare som skickas till createCallerFactory kommer att anropas före hanteraren som skickas till createCaller.
Hanteraren anropas med samma argument som en felformaterare skulle få, förutom shape-fältet:
ts
ts
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';constt =initTRPC .context <{foo ?: 'bar';}>().create ();constrouter =t .router ({greeting :t .procedure .input (z .object ({name :z .string () })).query ((opts ) => {if (opts .input .name === 'invalid') {throw newError ('Invalid name');}return `Hello ${opts .input .name }`;}),});constcaller =router .createCaller ({/* context */},{onError : (opts ) => {console .error ('An error occurred:',opts .error );},},);// The following will log "An error occurred: Error: Invalid name", and then throw a plain error// with the message "This is a custom error"awaitcaller .greeting ({name : 'invalid' });
tsinitTRPC } from '@trpc/server';import {z } from 'zod';constt =initTRPC .context <{foo ?: 'bar';}>().create ();constrouter =t .router ({greeting :t .procedure .input (z .object ({name :z .string () })).query ((opts ) => {if (opts .input .name === 'invalid') {throw newError ('Invalid name');}return `Hello ${opts .input .name }`;}),});constcaller =router .createCaller ({/* context */},{onError : (opts ) => {console .error ('An error occurred:',opts .error );},},);// The following will log "An error occurred: Error: Invalid name", and then throw a plain error// with the message "This is a custom error"awaitcaller .greeting ({name : 'invalid' });